The other day, one of my clients asked me if taking collagen after a workout would be more beneficial in terms of recovery instead of using protein powder. This made me realize that there might be some confusion among people about when they should take collagen supplements and when they should opt for protein powder.
This article will review collagen and protein powders, their unique amino profile, and when to take each.
Let me introduce myself. I’m Jenn, a performance and wellness registered and licensed dietitian nutritionist based in the Twin Cities, Minnesota. I help active individuals and athletes fuel confidently by using an individual-focused approach to fueling and performance that is purpose-driven and non-restrictive.
Let’s dive in!
Protein 101
Before we dive into the differences between collagen and protein powder, we need to go through a quick protein refresher.
Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays several vital roles in our body. It helps to build and repair muscle, generate energy, produce hormones, make enzymes, deliver oxygen, and maintain and grow tissue. Skeletal muscle contains 40% of protein, 25% is in the body organs, and the remaining is primarily in the skin and blood.
Protein is made up of 20 amino acids. The body cannot make nine essential amino acids, so we must get them through food.
The nine essential amino acids are:
- histidine
- isoleucine
- leucine
- lysine
- methionine
- phenylalanine
- threonine
- tryptophan
- valine
A complete protein contains all 9 of the essential amino acids. All animal products are considered complete proteins, along with soy food, quinoa, and hemp
An incomplete protein contains some but not all of the essential amino acids. Collagen and most plant proteins are incomplete proteins.
This is why it is essential to eat a variety of protein-containing foods when meeting your protein needs. Protein needs vary depending on age, gender, weight, and activity level.
Below is a chart of protein needs based on activity for healthy and active adults. If you have certain medical conditions or are a highly trained individual, you may have differing protein needs, which we could address one-on-one during an appointment.
| RDA | 0.8 grams protein per kilogram body weight |
| Endurance Athletes | 1.2-1.4 grams protein per kilogram body weight |
| Strength Athletes | 1.6-1.7 grams protein per kilogram body weight |
| Average adults to support optimal health outcomes | 1.2-1.6 grams protein per kilogram body weight |
| Fat loss | 1.6-2.4 grams protein per kilogram body weight |
What is Collagen Powder?
Collagen is lower in protein and lacks the essential amino acid tryptophan. However, it contains more amino acids: glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. Which are used by the body to make the collagen found in skin, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels.
Vital Proteins is a popular collagen brand. It contains 18 G protein per serving and 20 G collagen peptides.
The typical amino acid profile of a serving of Vital Protein Collagen:
- Alanine: 1,462 milligrams
- Arginine: 1517 milligrams
- Aspartic Acid: 1192 milligrams
- Glutamic Acid: 2239 milligrams
- Glycine: 3719 milligrams
- Histidine: 144 milligrams
- Hydroxylysine: 217 milligrams
- Hydroxyproline: 2058 milligrams
- Isoleucine: 271 milligrams
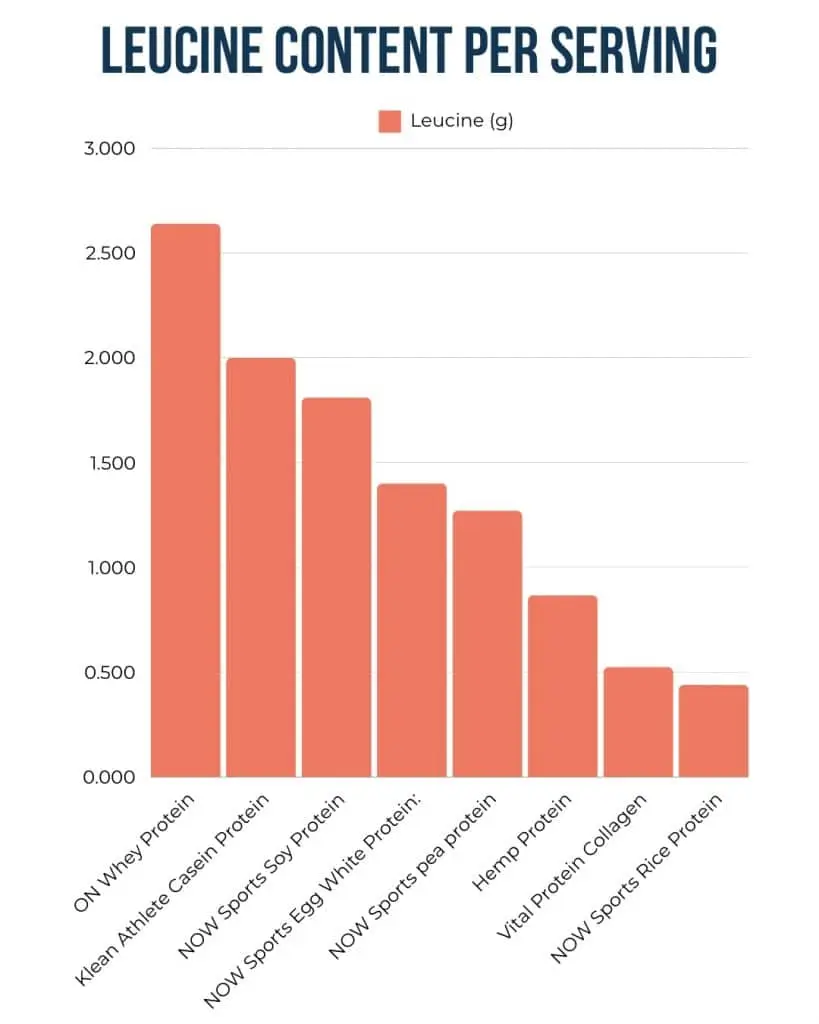
- Leucine: 524 milligrams
- Lysine: 614 milligrams
- Methionine: 108 milligrams
- Phenylalanine: 379 milligrams
- Proline: 2076 milligrams
- Serine: 614 milligrams
- Threonine: 343 milligrams
- Tryptophan: 0 milligrams
- Tyrosine: 90 milligrams
- Valine: 433 milligrams
What is Protein Powder?
Protein powders are typically a complete protein supplement that contains 15-25 grams of protein per serving.
The purpose of protein powders is to help fill in the gaps in the diet as a convenient way to increase your protein intake to reach your body composition goals.
The protein in the powder comes from various sources, including milk (whey or casein), plants (soybeans, peas, rice, or hemp), or eggs
Besides protein, protein powders often contain added sugars or sugar alternatives, flavorings, thickening agents, vitamins, and minerals.
Types of Protein Powder
Whey Protein Powder
Whey protein is a protein derived from cow’s milk. It is a well-researched protein that is known for being a high-quality protein that is highly bioavailable, quickly absorbed, and has benefits for muscle gain and recovery and cardiometabolic health
There are tons of different whey proteins on the market. You may have heard of whey concentrate and whey isolate protein powders, the most popular types of whey protein powders.
Typical amino acid profile in a serving of Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard 100% Whey Protein:
- Alanine: 1.16 grams
- Arginine: 0.56 grams
- Aspartic Acid: 2.79 grams
- Cystine: 0.56 grams
- Glutamic Acid: 4.45 grams
- Glycine: 0.45 grams
- Histidine: 0.45 grams
- Isoleucine: 1.68 grams
- Leucine: 2.64 grams
- Lysine: 2.38 grams
- Methionine: 0.49 grams
- Phenylalanine: 0.76 grams
- Proline: 1.46 grams
- Serine: 1.15 grams
- Threonine: 1.75 grams
- Tryptophan: 0.56 grams
- Tyrosine: 0.74 grams
- Valine: 1.39 grams
Casein Protein Powder
Casein protein is also found in cow’s milk that is digested and absorbed by the body slowly, unlike whey. The amino acid concentration peaks about 7 hours post intake, unlike whey, which peaks at 1-3 hours.
I recommend casein protein before bed for clients who want to help boost muscle growth and recovery while sleeping.
Typical amino acid profile in a serving of Klean Athlete Casein Protein:
- Alanine: 0.67 grams
- Arginine: 0.71 grams
- Aspartic Acid: 1.6 grams
- Cystine: 0.16 grams
- Glutamic Acid: 4.4 grams
- Glycine: 0.37 grams
- Histidine: 0.51 grams
- Isoleucine: 1.1 grams
- Leucine: 2.0 grams
- Lysine: 1.8 grams
- Methionine: 0.60 grams
- Phenylalanine: 0.99 grams
- Proline: 2.02 grams
- Serine: 1.2 grams
- Threonine: 0.91 grams
- Tryptophan: 0.31 grams
- Tyrosine: 1.04 grams
- Valine: 1.28 grams
Egg White Protein Powder
Egg white protein powder is less popular than whey or plant based protein powders.
Egg protein is highly bioavailable which means the body absorbs almost all the protein that the egg contains. Making it a good option for someone who has dairy sensitivities or doesn’t like the texture of plant based protein powders.
Typical amino acid profile in a serving of NOW Sports Egg White Protein:
- Alanine: 0.94 grams
- Arginine: 0.88 grams
- Aspartic Acid: 1.65 grams
- Cystine: 0.4 grams
- Glutamic Acid: 2.15 grams
- Glycine: 0.57 grams
- Histidine: 0.37 grams
- Isoleucine: 0.92 grams
- Leucine: 1.4 grams
- Lysine: 1.1 grams
- Methionine: 0.56 grams
- Phenylalanine: 0.95 grams
- Proline: 0.63 grams
- Serine: 1.12 grams
- Threonine: 0.74 grams
- Tryptophan: 0.2 grams
- Tyrosine: 0.63 grams
- Valine: 1.03 grams
Plant-Based Protein Powder
Pea Protein
Pea protein is a high-quality vegan and hypoallergenic protein made from ground-up yellow peas. A serving of pea protein typically contains about 15 grams of protein.
Typical amino acid profile in a serving of NOW Sports pea protein:
- Alanine: 0.64 grams
- Arginine: 1.31 grams
- Aspartic Acid: 1.82 grams
- Cystine: 0.14 grams
- Glutamic Acid: 2.71 grams
- Glycine: 0.62 grams
- Histidine: 0.39 grams
- Isoleucine: 0.73 grams
- Leucine: 1.27 grams
- Lysine: 1.12 grams
- Methionine: 0.16 grams
- Phenylalanine: 0.83 grams
- Proline: 0.68 grams
- Serine: 0.83 grams
- Threonine: 0.59 grams
- Tryptophan: 0.15 grams
- Tyrosine: 0.56 grams
- Valine: 0.78 grams
Soy Protein
Soy is a complete protein and one of the most well-studied plant-based proteins.
It also has a good leucine content, which means its effect on muscle growth is similar to whey protein.
Typical amino acid profile in a serving of NOW Sports Soy Protein:
- Alanine: 0.84 grams
- Arginine: 1.59 grams
- Aspartic Acid: 2.48 grams
- Cystine: 0.63 grams
- Glutamic Acid: 3.97 grams
- Glycine: 0.81 grams
- Histidine: 0.65 grams
- Isoleucine: 0.83 grams
- Leucine: 1.81 grams
- Lysine: 1.3 grams
- Methionine: 0.3 grams
- Phenylalanine: 0.93 grams
- Proline: 1.07 grams
- Serine: 1.09 grams
- Threonine: 0.69 grams
- Tryptophan: 0.36 grams
- Tyrosine: 0.77 grams
- Valine: 0.97 grams
Hemp Protein
If you are an athlete who gets tested, hemp protein is not a good choice for you since it comes from the same plant that marijuana comes from.
Although hemp on the market is from a strain with little THC, risking your athletic career is not worth it.
Hemp is not a pure protein product and contains around 10% fatty acids that are a balance of omega 6 and omega 3 fatty acids.
Typical amino acid profile in 100 grams of hemp protein (Keep in mind that 100 grams is about 3 servings of hemp protein) :
- Alanine: 3.85 grams
- Arginine: 15.52 grams
- Aspartic Acid: 12.53 grams
- Cystine: 0.2 grams
- Glutamic Acid: 2.4 grams
- Glycine: 2.1 grams
- Histidine: 1.1 grams
- Isoleucine: 1.0 grams
- Leucine: 2.6 grams
- Lysine: 1.4 grams
- Methionine: 1.0 grams
- Phenylalanine: 1.8 grams
- Proline: 1.8 grams
- Serine: 2.3 grams
- Threonine: 1.3 grams
- Tryptophan: 0.26 grams
- Tyrosine: 1.3 grams
- Valine: 4.53 grams
Brown Rice Protein
Brown rice is not a complete protein but is an option as long as you get a variety of proteins throughout your day.
For those with IBS, a rice protein may be a more suitable plant-based option if soy is not tolerated.
Typical amino acid profile in a serving of NOW Sports Rice Protein:
- Alanine: 0.29 grams
- Arginine: 0.42 grams
- Aspartic Acid: 0.42 grams
- Cystine: 0.09 grams
- Glutamic Acid: 0.92 grams
- Glycine: 0.21 grams
- Histidine: 0.12 grams
- Isoleucine: 0.21 grams
- Leucine: 0.44 grams
- Lysine: 0.18 grams
- Methionine: 0.14 grams
- Phenylalanine: 0.28 grams
- Proline: 0.24 grams
- Serine: 0.26 grams
- Threonine: 0.19 grams
- Tryptophan: 0.05 grams
- Tyrosine: 0.28 grams
- Valine: 0.28 grams
Collagen vs Protein Powder: Which is better?
Choosing collagen vs protein powder will depend on the timing and your goals.
Protein supplements are typically used after a workout to stimulate muscle protein synthesis.
However, collagen is not a good protein source to promote muscle protein synthesis after a workout because it lacks adequate amounts of certain amino acids, particularly leucine.
We want over 2 grams of leucine per serving along with a balanced array of other essential amino acids to help promote muscle protein synthesis.
Therefore, it is better to choose a protein powder made of whey, soy, or pea for post-workout recovery.
Collagen is more effective when taken at a dose of 15 grams with 50 milligrams of Vitamin C, 60 minutes before exercise to elevate collagen synthesis to potentially improve joint health.
Final Thoughts
It’s important to know that you don’t need a protein supplement to achieve your performance, body composition, or wellness goals. However, if you decide to use one, it’s essential to understand the difference between collagen and protein powder and when to use them.
If you have any questions about protein supplements, feel free to contact us today. You can also schedule an appointment to receive personalized nutrition advice to help you achieve your wellness and performance goals.
Jenn Fink is a licensed and board-certified Registered Dietitian Nutritionist based in Minnesota. Her goal is to help busy people and families prioritize their health by living a balanced lifestyle and feed their families flavorful meals without spending hours in the kitchen. Jenn is passionate about all things food-related and enjoys making complex science easy to understand for her clients and readers.

