Creatine is a widely used dietary supplement in performance nutrition. However, many wonder if they can get enough creatine through their diet alone and what foods are high in creatine?
This post will cover what creatine is, the benefits of creatine, how much you need, foods high in creatine, if you can get enough creatine through food, and creatine supplement recommendations.
Hey, I’m Jenn, a Registered Dietitian who has a passion for helping individuals fuel, think, and move towards the best versions of themselves without sacrificing their relationship with food. If you want practical, evidence-based nutrition advice to improve your performance and wellness — Learn how I can help.
Let’s dive in…
What is Creatine
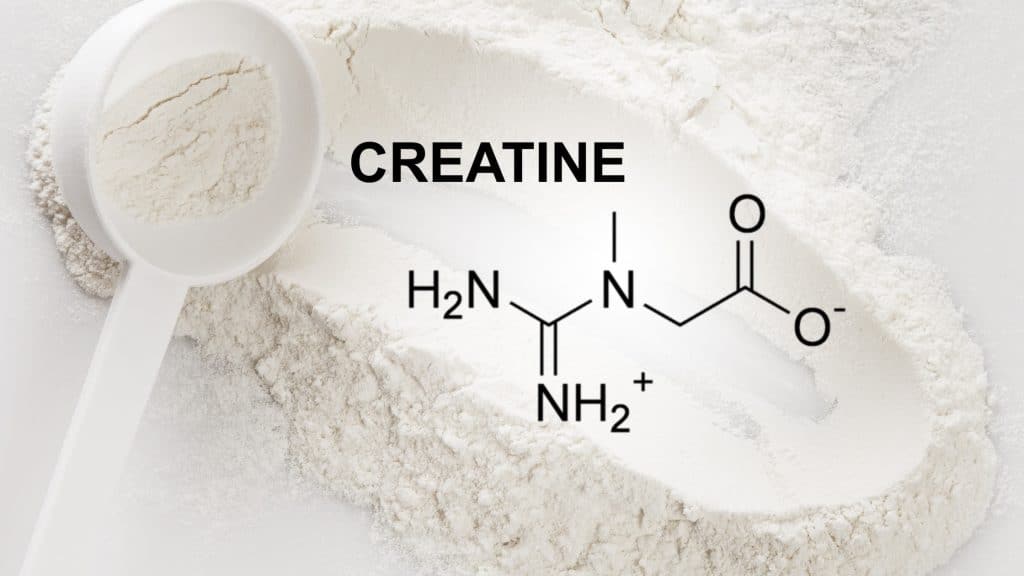
Creatine is a naturally occurring substance in specific foods that aids in the production of cellular energy that is stored as phosphocreatine in the muscles. Phosphocreatine serves as a phosphate source to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary source of energy for cells.
The body can also synthesize around 1-2 grams of creatine per day, using the amino acids methionine, glycine, and arginine. The majority of creatine, approximately 95%, is located in the skeletal muscles, while the remaining is found in the brain and testes.
Benefits of Creatine
Increased Muscle Strength and Power:
Creatine is widely recognized for its ability to boost muscle strength and power. By replenishing ATP stores more quickly, creatine helps users to push themselves harder during workouts, leading to greater strength gains and increased power output.
Increased Muscle Mass:
Creatine is a supplement that not only boosts your body’s ability to perform high-intensity exercises but also encourages muscle growth by elevating water content within muscle cells. This results in an upsurge of intracellular hydration, protein synthesis, and eventually, muscle mass.
Improved High-Intensity Performance:
Whether you’re an athlete or someone who enjoys high-intensity training like HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training), incorporating creatine into your routine can significantly enhance your overall performance. By increasing the availability of ATP during intense exercise, individuals experience reduced fatigue and prolonged endurance capacity.
Enhanced Recovery:
Creatine can be useful for promoting recovery after a workout. It works by facilitating the resynthesis of ATP while simultaneously reducing inflammation markers such as cytokines and myostatin levels in the body. This leads to quicker recovery between workout sessions or competitive events.
Enhanced Mood & Cognition Effects:
Apart from the physical performance benefits, research has shown that creatine may have neuroprotective properties that could enhance cognitive function and brain health. In addition, there have been indications that creatine may aid in the treatment of neurological disorders.
Increased Bone Health:
New research has demonstrated a potential of positive effects of creatine on bone health but more research is needed. Studies indicate that creatine supplementation has the potential to improve bone mineral density, making it a particularly useful supplement for athletes as well as individuals concerned about osteoporosis or age-related bone loss.
How Much Creatine Do You Need?
Typically, a diet providing 1-2 grams of Creatine per day can saturate muscle Creatine stores by 60-80% through dietary sources and body synthesis. However, to fully optimize muscle Creatine stores, an additional 3-5 grams of Creatine Monohydrate supplementation per day is recommended.
Studies have shown that taking Creatine with a carbohydrate source or a combination of carbohydrate and protein sources could improve Creatine retention.
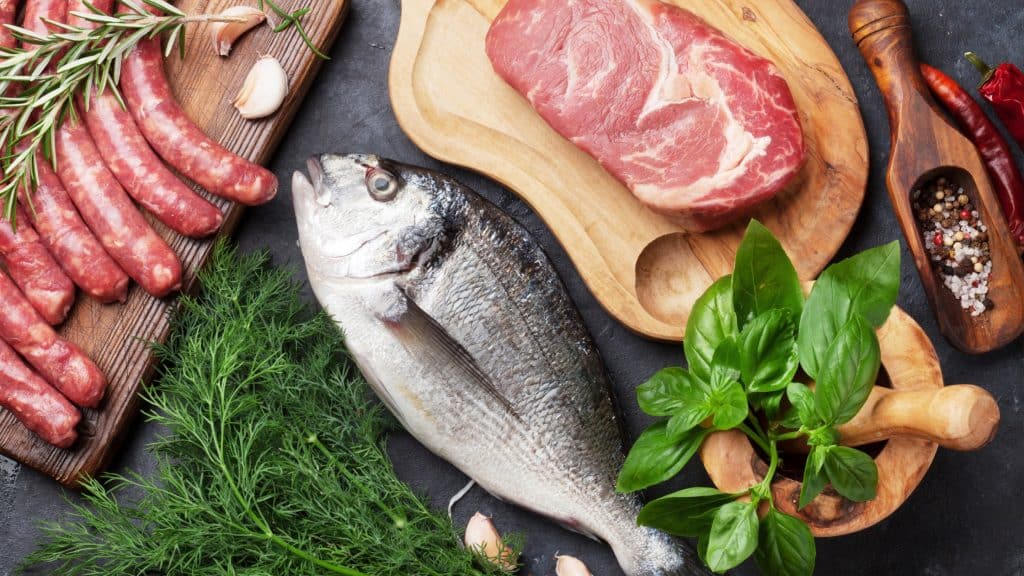
Foods High in Creatine
Creatine is naturally found in certain foods such as milk, steak, and some types of fish. Herring contains the highest amount of creatine at 3.0-4.5 grams of creatine per pound. Beef, pork, tuna, salmon, and cod contain between 1.4 to 2.3 grams of creatine per pound.
Here is a list of foods high in Creatine:
- Herring: 3.0-4.5 grams per pound
- Pork: 2.3 grams per pound
- Beef: 2.0 grams per pound
- Salmon: 2.0 grams per pound
- Tuna: 1.8 grams per pound
- Cod: 1.4 grams per pound
- Milk: 0.05 grams per pound
- Shrimp: Trace amounts

Can You Get Enough Creatine From Food?
While you can obtain creatine through food, it’s nearly impossible to consume the recommended daily dose in this way. The amount of creatine you obtain from food is significantly less than what’s needed to maximize your creatine stores.
In fact, once you start cooking beef, pork, or fish, the creatine content decreases significantly. To achieve the recommended Creatine intake, you would need to consume approximately 2.5 pounds of raw beef – which I DO NOT recommend.
Instead, consider creatine supplementation as a safer and more effective alternative.
Best Creatine Supplements According to a Dietitian
If you’re on the hunt for a creatine supplement, there are a few things you should keep in mind. First, check that the supplement contains only creatine monohydrate as an ingredient. Additionally, ensure that it has undergone third-party testing and bears either the NSF certified sport or Informed Sport logo.
As a performance dietitian, my go-to recommendations for creatine supplements are Thorne’s creatine and Klean Athlete’s creatine.
Final Thoughts
Although some raw foods are high in creatine, cooking significantly reduces their creatine content. Depending solely on food intake to meet your recommended creatine dosage is not practical.
Therefore, if you’re considering taking a supplement, it’s advisable to first consult with a dietitian. This ensures that you are consuming enough energy from your diet to get the most out of the supplement.
Are you ready to stop stressing about your diet and learn realistic strategies that work? Schedule a free 15 minute call today!
Jenn Fink is a licensed and board-certified Registered Dietitian Nutritionist based in Minnesota. Her goal is to help busy people and families prioritize their health by living a balanced lifestyle and feed their families flavorful meals without spending hours in the kitchen. Jenn is passionate about all things food-related and enjoys making complex science easy to understand for her clients and readers.

